IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) continues to play a vital role in modern networking, even as IPv6 adoption grows. Its structured addressing system, divided into distinct classes, ensures efficient network management and scalability. For businesses and network administrators, understanding IPv4 address classes is essential—especially when leasing IPv4 addresses to meet dynamic network requirements.
In this blog, we’ll explore the different IPv4 address classes, their uses, and why leasing IPv4 addresses is a smart choice for businesses. We’ll also answer some frequently asked questions about IPv4 leasing.
What Are IPv4 Address Classes?
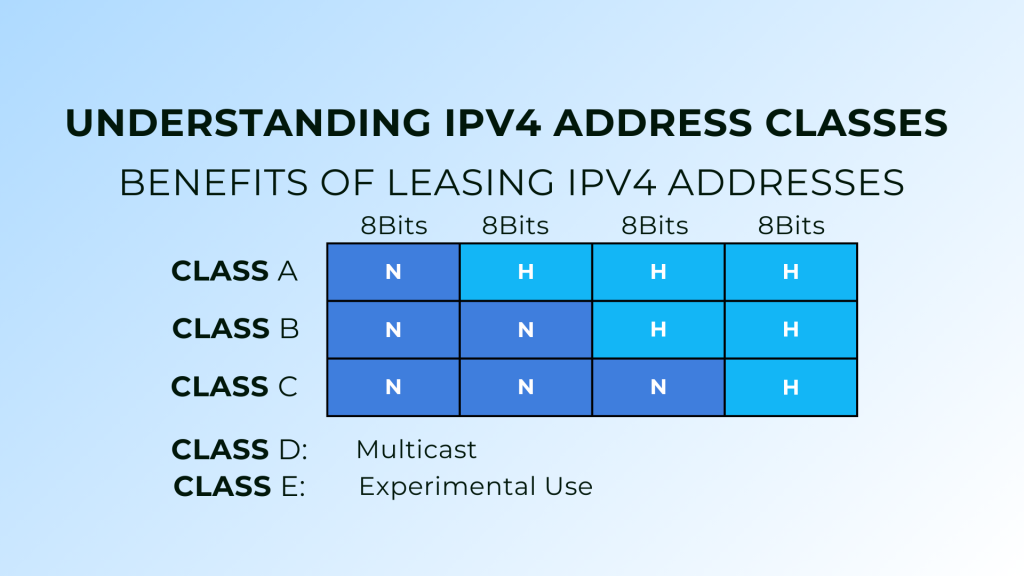
IPv4 addresses are 32-bit numerical identifiers represented in a dotted decimal format (e.g., 192.168.1.1). These addresses are divided into five main classes: A, B, C, D, and E. Each class is designed for specific networking purposes, catering to different scales of network operations.
Breakdown of IPv4 Address Classes
Class A
Range: 1.0.0.0 to 126.0.0.0
Default Subnet Mask: 255.0.0.0
Network/Host Division: 8 bits for the network, 24 bits for the host
Usage: Ideal for large organizations and ISPs, supporting up to 16 million hosts per network. Leasing Class A addresses is perfect for businesses with extensive device requirements.
Class B
Range: 128.0.0.0 to 191.255.0.0
Default Subnet Mask: 255.255.0.0
Network/Host Division: 16 bits for the network, 16 bits for the host
Usage: Designed for medium-sized networks, such as universities and large enterprises. Leasing Class B addresses offers a balance between scalability and cost-effectiveness.
Class C
Range: 192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.0
Default Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Network/Host Division: 24 bits for the network, 8 bits for the host
Usage: Best suited for small businesses, supporting up to 254 hosts per network. Leasing Class C addresses is an affordable option for startups and private networks.
Class D
Range: 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255
Usage: Reserved for multicast applications, such as streaming, gaming, and real-time communication. These addresses are not typically leased for traditional networking needs.
Class E
Range: 240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
Usage: Reserved for experimental purposes and not available for general use.
Why Leasing IPv4 Addresses Makes Sense
With the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses, leasing has become a strategic option for businesses. Here are the key benefits of leasing IPv4 addresses:
Flexibility: Scale your network without committing to purchasing IP addresses.
Cost-Effectiveness: Pay only for what you need, making it ideal for temporary projects or growing businesses.
Scalability: Choose from Class A, B, or C leases to address different network sizes.
Leasing IPv4 Addresses by Network Size
Large Networks: Opt for Class A or B addresses to support expansive systems.
Small to Medium Networks: Class C addresses provide affordable scalability for businesses with moderate requirements.
Reserved IPv4 Address Ranges
Certain IPv4 address ranges are reserved for specific purposes:
Private IPs (RFC 1918):
Class A: 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255
Class B: 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
Class C: 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
These addresses are used in private networks and are non-routable on the public internet.
Loopback Address: 127.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255 (used for internal testing).
APIPA: 169.254.0.0 – 169.254.255.255 (self-assigned when no DHCP server is available).
Conclusion
Understanding IPv4 address classes is crucial for optimizing network performance. Leasing IPv4 addresses offers businesses a flexible and scalable solution to adapt to changing network demands. Whether you’re managing a startup or a large-scale enterprise, partnering with a trusted IPv4 leasing provider ensures your network operates seamlessly.
FAQs About IPv4 Address Classes and Leasing
IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses, while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses. IPv6 was introduced to address the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses and offers improved security and scalability.
No, Class D addresses are reserved for multicast applications, and Class E addresses are for experimental purposes. These classes are not available for leasing.
The choice depends on your network size:
Large networks: Class A or B
Medium networks: Class B
Small networks: Class C
No, private IPv4 addresses (RFC 1918) are non-routable on the public internet and are intended for internal network use.
Yes, leased IPv4 addresses are as secure as purchased ones. Ensure you work with a reputable provider to maintain security and compliance.